

 2021-03-04
2021-03-04
Contains Nonbinding Recommendations
This draft guidance, when finalized, will represent the current thinking of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA, or the Agency) on this topic. It does not establish any rights for any person and is not binding on FDA or the public. You can use an alternative approach if it satisfies the demands of the applicable statutes and regulations. To discuss an alternative approach, contact the Office of Generic Drugs.
Active Ingredient: Sevelamer carbonate
Dosage Form; Route: Tablet; oral
Overview:
This draft guidance provides recommendations for developing a generic drug product, sevelamer carbonate tablets, using sevelamer carbonate as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
First, FDA provides recommendations for supporting a demonstration of API sameness. Second, FDA provides recommendations for demonstrating bioequivalence of this product.
Recommendations for Demonstrating API Sameness:
1. The API, sevelamer carbonate, is a polymeric drug substance. According to the labeling of the reference listed drug (RLD), (Renvela®), sevelamer carbonate has the same polymeric structure as sevelamer hydrochloride, in which carbonate replaces chloride as the counter ion. Because sevelamer hydrochloride is poly(allylamine hydrochloride) crosslinked with epichlorohydrin, FDA encourages sponsors to follow the same synthetic route to manufacture the API.
2. Otherwise sponsors should contact the Office of Generic Drugs (OGD) to obtain concurrence for a proposed alternative synthetic route, which may require characterizations in addition to the ones outlined in the current draft guidance to demonstrate API sameness.
3. Sameness of sevelamer carbonate can be established based on its synthetic route and comparative physico-chemical characterizations. The information on manufacturing process and in-process controls should be provided to the Agency. The sponsor is advised to perform side-by-side comparative testing using the Test API and the API extracted from the RLD product. The method of API extraction should be documented and submitted to the Agency in the abbreviated new drug application (ANDA). At least three batches of the Test API and at least three batches of the extracted RLD (Reference) API should be characterized to assess API sameness and robustness in the manufacturing process.
4. Based on the data generated from the characterization, the sponsor should define and prove the chemical structure and molecular formula of the Test API in comparison to the Reference API. A schematic representation of sevelamer carbonate is shown in Figure1. The sponsor should measure and report the individual parameters (i.e., a, b, and c) associated with various molecular sub-groups in the schematic.
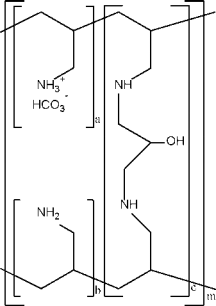
Figure 1. Chemical Structure of Sevelamer Carbonate
a, b = number of primary am^ne groups a + b = 9
c = number of crosslinking groups c = 1
m = large number to indicate extenjej polymer network
The methods and results of the following characterizations of the Test and the Reference APIs should be reported to the Agency. The claim of API sameness should be supported by comparative characterization results of the Test and Reference APIs.
1. Degree of crosslinking (i.e., ratio of crosslinked amine groups to total amine groups): The Agency recommends that sponsors use13C Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (13C SSNMR) spectroscopy to quantify the degree of crosslinking in the APIs by quantitative peak-area analysis.
2. Degree of protonation (carbonate content): Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is recommended to measure the degree of protonation.
3. Total titratable amine: Titration is recommended to quantify the total-titratable-amine content.
4. Particle size: Particle size distributions of the APIs should be reported.
5. Elemental analysis: The results should include C, H, and N elements.
6. Swelling index: The range of swelling index of the APIs should be reported.
7. The sponsor is also encouraged to perform additional characterization including, but not limited to, Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, X- ray diffraction (XRD), and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to further characterize the chemical structure and physico-chemical properties of the APIs.
Recommendations for Demonstrating Bioequivalence:
Recommended studies: 2 in vitro studies
1. Type of study: In vitro equilibrium binding study
Design: With and without acid pre-treatment at pH 4 and pH 7
Strength: 800 mg
Subjects: Not applicable (N/A)
Additional comments: The equilibrium binding study is considered the pivotal bioequivalence (BE) study. This study should be conducted by incubating the Test and Reference products with at least eight different concentrations of phosphate, with and without acid pretreatment, at pH 4 and pH 7. Whole tablets should be used in the study. Each phosphate incubation medium should contain 80 mM NaCl and 100 mM N,N-Bis (hydroxyethyl)-2aminoethanesulfonic acid (BES). Phosphate concentrations should be spaced along the spectrum until the maximum binding is clearly established. All incubations should be conducted at 37°C. Each binding study should be repeated at least 12 times. In addition, data should be provided demonstrating that the length of time selected for incubation with the phosphate-containing medium yields maximum binding.
Additional details on a similar equilibrium binding study design are available in the cholestyramine powder/oral guidance. Also see Swearingen et al., “Determination of the Binding Parameter Constants for Renagel® Using the Langmuir Approximation at Various pH Values by Ion Chromatography.” J. Pharm. Biomedical Anal. 29 (2002), pp. 195-201.
2. Type of study: In vitro kinetic binding study
Design: With and without acid pre-treatment at pH 4 and pH 7
Strength: 800 mg
Subjects: N/A
Additional comments: The kinetic binding study should be used to support the pivotal equilibrium binding study. This study should be conducted by incubating the Test and Reference products for at least eight different lengths of time, with two different phosphate concentrations, with and without acid pre-treatment, at pH 4 and pH 7. Whole tablets should be used in the study. The phosphate concentrations used in each kinetic binding study should be the lowest and highest used in the corresponding equilibrium binding study.
Each incubation medium should contain 80 mM NaCl and 100 mM N,N-Bis (hydroxyethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid (BES). Times should be selected along the spectrum until the maximum binding is clearly established. All incubations should be conducted at 37°C. Each binding study should be repeated at least 12 times.
Additional details on a similar equilibrium binding study design are available in the cholestyramine powder/oral guidance. Also see Swearingen et al., “Determination of the Binding Parameter Constants for Renagel® Using the Langmuir Approximation at Various pH Values by Ion Chromatography.” J. Pharm. Biomedical Anal. 29 (2002), pp. 195-201.
Analytes to measure: Unbound phosphate in filtrate (to calculate phosphate bound to resin)
For the in vitro equilibrium binding study, the Langmuir binding constants ki and k2 should be determined. The Test/Reference ratio should be calculated for ki. The 90% confidence interval should be calculated for k? with the acceptance criterion of 80% to 120%.
For the in vitro kinetic binding study, the Test/Reference bound phosphate ratios at the various times should be compared but not subjected to the 90% confidence interval criterion.
Bioequivalence based on (90% CI): The Langmuir binding constant k2 from the equilibrium binding study.
Waiver requests of in vitro equilibrium and kinetic binding studies: N/A
Dissolution test method and sampling times: N/A
Disintegration Test: A Dissolution Methods Database is available to the public at the FDA- Recommended Web site AT http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/dissolution/. Information about regulatory disintegration testing for this product is available at this Web site. Conduct comparative disintegration testing on 12 dosage units each of all strengths of the Test and Reference products. Specifications will be determined upon review of the application